ASTM D3273 Fungal Resistance Test for Coated Surfaces
Get A Testing Quote
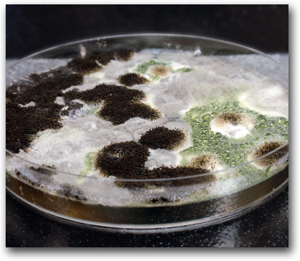 The ASTM D3273 method is meant to evaluate fungal defacement of coated interior surfaces in an accelerated manner. The ASTM D3273 test specifically aims to establish the relative resistance of paint films to the propagation of mold and mildew under optimum fungal growth conditions. Incubation occurs in a highly regulated environmental chamber of standardized dimensions over a 4-week period.
The ASTM D3273 method is meant to evaluate fungal defacement of coated interior surfaces in an accelerated manner. The ASTM D3273 test specifically aims to establish the relative resistance of paint films to the propagation of mold and mildew under optimum fungal growth conditions. Incubation occurs in a highly regulated environmental chamber of standardized dimensions over a 4-week period.
For this test, the product is suspended above a bed of spore-inoculated soil within a chamber kept at high humidity. A coating which does not protect against fungal growth should exhibit surface defacement evidenced by fungal hyphae (filaments) visible on the surface after 4 weeks of incubation. This test emulates realistic conditions for coatings designed for use in interior environments.
Summary of the ASTM D3273 Test Method
- The environmental growth chamber is equilibrated for a 24 hour period at approximately 32°C with proper soil and water content
- Mold suspensions from 3 fungi cultures are spread evenly over soil surface and allowed to incubate for 14 days. Aureobasidium, Aspergillus niger, and Penicillium species are used.
- Coated test panels and non-coated substrates are introduced randomly to the sporolating chamber by vertical hanging.
- Panels are rated once a week for 4 weeks by estimating the level of fungal defacement on a scale of 0 to 10 (10 is no visual defacement).
- The standardized rating system is covered by ASTM D3274, which complements the ASTM D3273 test method.
Strengths of the ASTM D3273 Test Method
- ASTM D3273 offers accelerated growth for higher throughput testing.
- The method provides stringent testing conditions to mimic an extreme environment.
- The test can easily be adapted to include several species of fungus for custom projects.
- The test offers a straigtforward methodology to control for extraneous variation.
- The test uses easily accessible, low-tech tools and standard microbiology supplies.
- Several samples can be tested in one chamber.
- Provides ~ 95% confidence in a product’s ability to resist fungal growth.
Weaknesses of the ASTM D3273 Test Method
- The method is designed specifically to test paint and varnishes which can exclude a range of other products.
- This test uses only 3 fungal spores which doesn’t account for the potential myriad spores found in nature.
- ASTM D3273 compares growth under static temperature and humidity parameters, whereas real product usage may be better represented by a range of temperature and humidities in some instances.
- The method doesn’t account for real-world conditions due to human activities, such as regular cleaning of the surface.
- The test offers little information about product’s long-term performance
- The scoring system is subject to interpretation which can lead to variability across labs.
Microchem Laboratory hopes that you have found this ASTM D3273 test method resource page to be helpful. If you are interested in testing an antifungal substrate rather than an antifungal coating, please note that this method can be used as a basis for customized antifungal testing. Such custom tests can produce a relative measure of fungal resistance can still be established. Alternatively, the ASTM G-21 fungal resistance test can be used.
