Microchem Laboratory is one of just a few labs in the US to provide custom aerobiological testing services for antimicrobial devices and chemicals.
Our laboratory has the capacity to perform testing with UV devices designed to decontaminate an entire room or with devices as small as a tabletop microbial sampler. We strive for excellence by providing knowledgeable staff with a variety of testing chambers and a diverse collection of microorganisms to provide clients with fast, reliable data.

The majority of studies done by our laboratory consist of treating aerosolized microorganisms with antimicrobial devices, chemicals, or a combination of both. For example, a bioaerosol containing a regulated concentration of microorganisms is generated within a containment chamber to test the ability of an ultraviolet light to kill airborne bacteria.
Once the device is run, an air sample is taken to determine the viable microbial counts recovered from the air. Testing such as this is performed regularly at Microchem by a small team of scientists. Successful generation and containment of aerosolized microorganisms requires considerable microbiological expertise. Our small team structure allows a few scientists to become experts at aerosol testing, ensuring each project is handled by experienced personnel at Microchem.
As a general rule, Microchem Laboratory does not run aerosol studies using infectious microorganisms. However, the laboratory routinely runs aerosol tests using surrogates and indicator organisms. For instance, MS2 bacteriophage is an excellent surrogate for viruses that may be spread through the air, such as Rhinovirus, the virus which causes the common cold. Microchem Laboratory is always willing to discuss projects and find solutions that meet your aerobiological testing goals.
Testing Chambers
Microchem Laboratory maintains a custom-built aerosol testing chamber. It has been used to test antimicrobial products ranging from air filters to ultraviolet lights to ion-generating technologies. The aerosol testing chamber is particularly useful for determining the effect of antimicrobial agents on microorganisms present individually or in small clusters in the air, as bioaerosols.
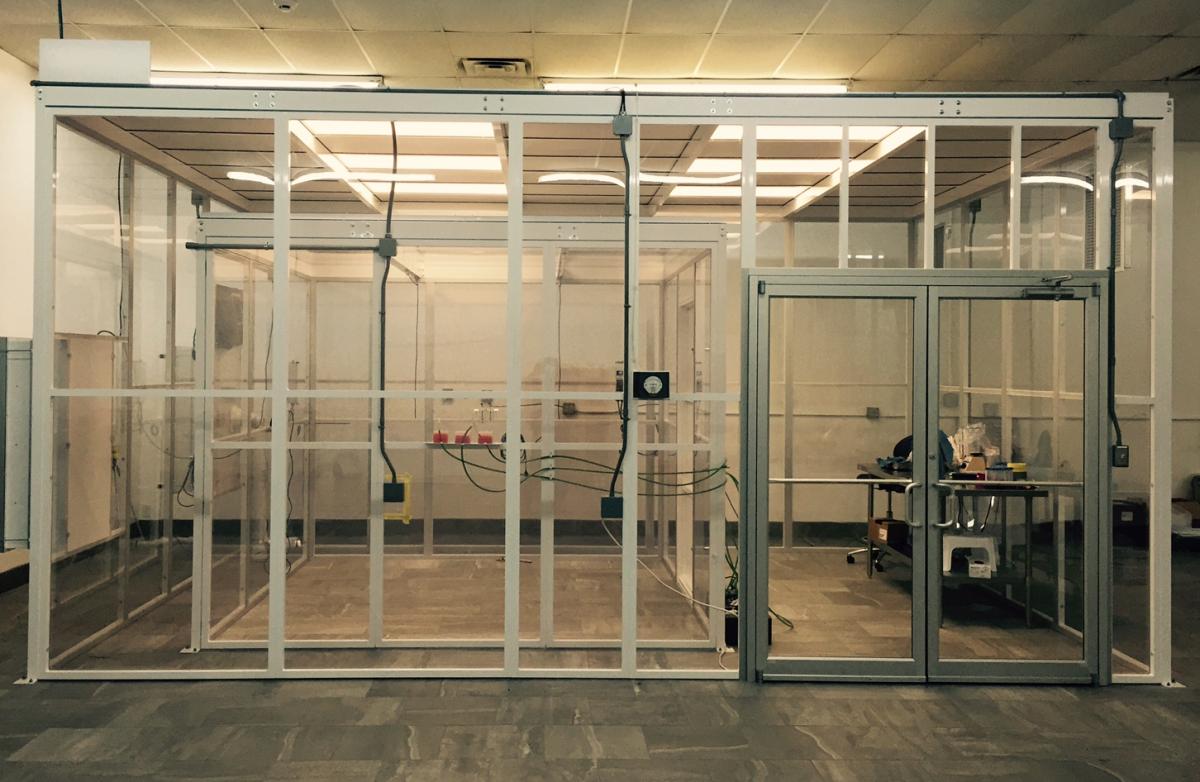

The inner chamber is affectionately referred to as the NPAC (Negative Pressure Aerosol Chamber). It measures 10′ x 10′ x 8′ (800 cubic ft.), which is the standard size for a room according to the EPA. Testing conducted in the NPAC simulates life size testing of whole room disinfection devices against aerosolized bacteria, fungi, or viruses.
Studies can be modified in a multitude of ways by adjusting parameters within the chamber. For example, the aerosol input can be brief or continuous, the air can be continually mixed or static, and the humidity or temperature can be adjusted. The concentration of germs and the species of microorganism can be modified. New microorganisms, especially species with questionable pathogenicity, are considered cautiously before aerosol testing is allowed. However, scientists at Microchem are willing to work with companies that are interested in testing specific germs for aero-biologic research.

Along with the large NPAC chamber, there are two additional smaller chambers, the cube and the 4′ x 4′. These two smaller chambers were designed to accommodate small devices, such as microbial samplers or air scrubbers. The cube measures exactly one cubic meter, this size allows for easier calculations to determine microbial counts in the air. The 4′ x 4′ chamber, pictured to the right, is named for it’s size. This chamber is used more often and has been modified to allow scientists to interact with devices while inside the chamber. In the large NPAC chamber, although it more closely simulates an actual room, devices must be controlled remotely. The 4′ x 4’s modifications to allow for direct interaction, can be a benefit to some clients whose devices do not have this option.
All chambers are decontaminated fully at the end of each aerosol run and no laboratory personnel may enter or open a chamber until it has been decontaminated. The decontamination method has been verified with internal validation tests for each of the germs used for aerobiological testing. Safety is of utmost importance at Microchem Laboratory and aerosol testing is not an exception.
The Microbial Challenge
Germs are everywhere; they surround us in our everyday lives. Most bacteria are harmless to humans and in fact help us with many aspects of daily life. They thrive in our gut to aid with digestion of food, they ferment our alcoholic beverages, and they break down bio-hazardous material in the water treatment process. On the other hand, some bacteria can make humans very sick.
Microorganisms that cause disease are referred to as pathogens. Although there are fewer pathogenic species compared to the microorganisms that are benign, bacteria, fungi, and viruses that cause diseases are more recognizable due to their infamy. Combating the more virulent microorganisms involves extensive antibiotic therapy unless infection can be mitigated with vaccination of a large number of the population to avoid outbreaks or diligent disinfection in high risk areas such as hospitals.
Infectious microorganisms are most dangerous when transmitted through the air. They are invisible to the naked eye and exist everywhere. If an infected person sneezes they have aerosolized an unknown number of virulent microorganisms. There are limited options when trying to control bacteria once it has been aerosolized.
The following list includes some of the microorganisms that are pathogenic and have the potential to become aerosolized:
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis, TB
- Bordetella pertussis, Whooping cough
- Haemophilus influenzae, Opportunistic bacterial pathogen
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Adaptive bacteria which causes many diseases
- Influenza, Flu causing virus
- Rhinovirus, Common cold virus
- Aspergillus, Fungal lung infections called Aspergillosis
At Microchem Laboratory, we do not aerosolize pathogens. However, we have many surrogates to choose from that are representative of pathogenic microorganisms but with considerably less risk to scientists. For more information about the bacteria, viruses, and fungal species that are aerosolized at the lab, contact the laboratory and speak with one of our knowledgeable scientists.
Industry Innovations Require a Flexible Team for Antimicrobial Testing
The Microchem Laboratory approach to scientific research is a small team structure that promotes collaboration and innovative thinking. Our unique company structure allows our clients to work with a specific team which specializes in the type of antimicrobial testing most relevant to our client’s project. All of Microchem’s scientists have access to many years of experience from management and other microbiologists at the laboratory promoting synergy across the many teams. Scientists from each team have developed an expertise for each area of testing covered by Microchem, treated articles, disinfectants and sanitizers, virology, and custom device testing. The small team structure facilitates the collaborative environment promoted by management and implemented by employees. Microchem’s belief that the scientist should be the primary source of communication for our clients streamlines the planning processes for testing, keeps communication open, and alleviates the stresses of a middle-man. Each project is approached individually and the scientist maintains a client’s goals at the forefront of decisions.
Microchem Laboratory has a four team structure; each team specializes in a different area of antimicrobial testing. Our disinfectants and sanitizers team specializes in testing standard disinfectants and sanitizers under GLP, Good Laboratory Practice, conditions. Treated articles team handles any and all fabrics or surfaces that have label claims of antimicrobial properties, contact the laboratory to find out more about the treated articles exemption. The laboratory also has a team of dedicated virologists who would welcome the chance to speak with clients about their products potential as an antimicrobial agent registered to eliminate viruses. The fourth team consists of scientists most familiar with custom devices and aerosol testing. In addition to the teams and the management personnel, Microchem also has its own quality assurance unit, who performs internal audits on all GLP projects.
Aerosol testing services are under the custom teams jurisdiction. Being a part of the custom team generally involves thinking outside of the box, since scientists on this team see devices and products that fall outside of the normal realm of regulations. The main goal of our custom team is to answer any question a study sponsor would like to ask with innovative yet challenging set of parameters.

With our experienced and knowledgeable scientists, our facilities are able to accommodate almost any testing request. The 15,000+ square foot building has been able to encompass all four teams working simultaneously. The building contains offices, meeting rooms, a classroom, a test room dedicated to devices, and an entire area, nearly a third of the entire building, dedicated to aerosol testing.
In addition to our staff and facilities, the resources accessible to the scientists ensures studies can be as complex and far-reaching as the imagination of our clients. Our extensive microbial library allows access to microorganisms which best suit the testing desired. If Microchem does not have the specific organism our client’s testing requires, our scientists would be happy to acquire the organism. Studies contracted at our facility will have customized parameters to suit our client’s needs and will be performed to the highest standards by our experienced scientists.
Aerobiological Testing and the EPA
Aerosol testing conducted at Microchem Laboratory typically involves the use of devices, such as UV whole room disinfection devices. Devices fall under special regulations according to the EPA. Visit our Whole Room Disinfection page to learn more about the EPA’s regulations and how these regulations affect devices.
Currently, no standard method exists for aerosolizing bacteria. There are limited guidelines on how testing should be conducted, how results should be calculated, or how to decontaminate an aerosol chamber. At Microchem, we pride ourselves on incorporating state of the art equipment, such as the custom built chambers, with highly educated staff who specialize in aerosol generation to complete complicated experiments in timely and cost-effective manner. An Microchem scientist can suggest steps to follow for making aerosol claims on labels but we always recommend working with a consultant or contacting the EPA directly.
Requiring strong regulatory knowledge for a less-regulated sector might seem counterintuitive but it’s essential when making label claims. Regulatory agencies allow custom and aerosol studies to be submitted in claim packets but approval of a protocol prior to testing by the agency is recommended. With no standard method to follow, testing validity for custom studies may come into question once submitted to the EPA, even under GLP conditions. Understanding intimately the registration process or having a consultant available to explain the EPA guidelines is an excellent way to ensure the process runs smoothly. Consulting with a laboratory that is GLP-compliant, already in possession of a robust Quality Management System, successfully EPA and third party audited, and up-to-date with new regulatory advances, will make your antimicrobial testing run efficiently and within compliance.
How to Navigate the Antimicrobial Testing Process
At Microchem Laboratory, we pride ourselves on our excellent service, our expedited turn around times, and our flexibility. We want to share our passion for science with our clients, and the most effective way to do this is to leave every client satisfied with the testing services provided. Navigating the testing process can be a tricky path, but a Microchem scientist is waiting to assist clients with their testing goals. In order to better understand our start to finish service model, the following graphic provides a visual interpretation of the steps followed at the laboratory.
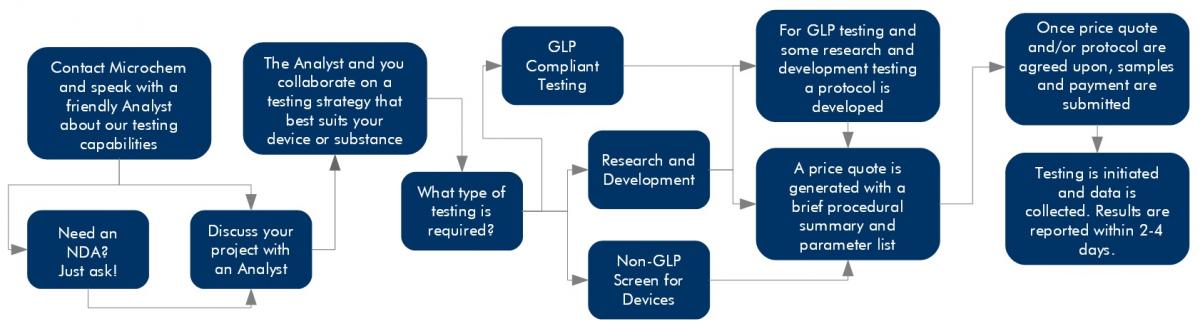
Once a client has contacted the laboratory, either by calling (512) 310-TEST or by inquiring through our online form, discussion about the client’s goals will be handled by the team most closely related to the desired testing. If the product or device is confidential, Microchem has an established NDA agreement we can customize for our clients or we are willing to work with our client’s existing NDA documentation. At Microchem Laboratory, all of our scientists take confidentiality seriously. We would like our clients to feel comfortable discussing their devices or projects they have worked hard to develop. Feel free to inquire about establishing a non-disclosure agreement if necessary.
If our clients have a desire to make a claim, we will recommend GLP testing and the EPA will require it. Scientists at Microchem have a respectable understanding of the EPA’s regulations. We always recommend meeting with a consultant but are happy to answer as many questions about antimicrobial testing regulations as we can. If the product, has not already been registered and limited antimicrobial testing has been performed, Microchem will recommend a non-GLP screen to help establish confidence before moving into GLP testing.
After gathering contact information, the scientist will produce a detailed price quote that outlines parameters and breaks down the pricing. Microchem Laboratory has a set pricing structure that ensures standardized prices for all. Upon approval of the parameters and price, a testing timeline will be established. Depending upon the method or the complexity of a study, our scientists will determine an accurate timeline and communicate this directly to our client. If testing needs to be expedited, Microchem will ensure deadlines are met for data to the best of our capabilities.
Once the test substance, or device, and payment are received, testing will begin. Our client’s have access to their scientist at all stages of testing. Longer running experiments will be accompanied with regular updates and after all data has been gathered a final report. While shorter tests will only include a final report. If any hiccups occur or if our client would like to change a parameter, scientists are always available to discuss the shift in testing.
Results are calculated and laid out in a report format which reflects the type of testing conducted, non-GLP or GLP. In addition, the scientist who ran that study will discuss the results directly with the clients. Any questions can be answered about reporting or the outcome of the study, as well as open the dialog to additional testing or if this was a non-GLP screen, discussion of the GLP process can happen at this time.
For additional information about the antimicrobial testing process or to inquire about testing please contact the laboratory.
References
https://www.epa.gov/
Written by: E. Richard B.S.
